The active steering system for the rear axle, integrated with the car's steering system, equips more and more vehicles: from the Porsche 911 GT3/RS to the Ferrari 812 Superfast or even the latest Renault Mégane RS.
These systems are not new. From the first passive steering systems to the latest active systems, the path of development and cost containment of this technology has been a long one, but ZF has developed what will be the first active steering system to comprehensively equip production vehicles.
Brand considerations aside, one of the most awarded car component manufacturers in the world (8th consecutive title in 2015), ZF, revolutionized active steering systems for the rear axle with a natural evolution of previous systems, cheaper and less complex.
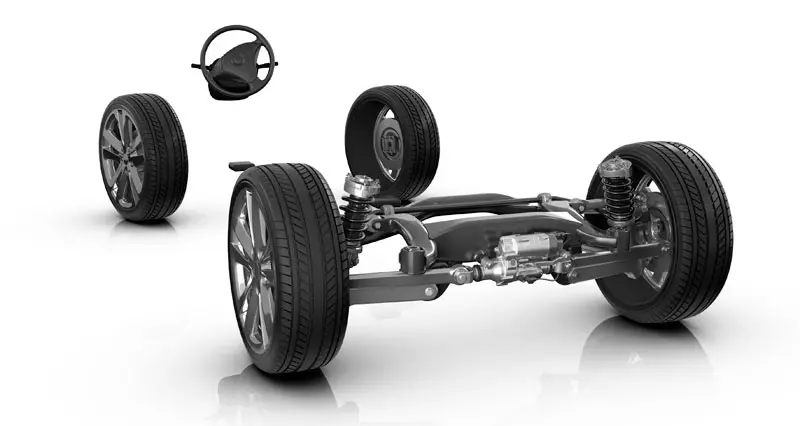

What does the ZF steering system consist of?
Acronyms and nomenclatures aside, we will see many brands using the base of the ZF steering system, which internally is called AKC (Active Kinematics Control). From brand to brand, it changes the name but it will be the same system.
The name ZF gave it even gives us a good clue about the nature of this system. From the control of kinematic forces, we can immediately infer that the system acts on the force of movement, but we do not want to dwell on issues of Applied Physics or Basics of Classical Mechanics. Please do not…
This system is controlled by a control module (ECS) which is in charge of actively managing, through parameters received by sensors of speed, wheel angle and steering wheel movement — all functions in the variation of the toe-in angle in the rear wheels.
This same variation in the angle of convergence of the rear wheels can go up to 3º of difference between positive and negative variations. That is, with a negative angle, the wheels seen from above have a convex alignment forming a V, where the vertex of this same V represents the angle at 0°, projecting the opening of the wheels outwards. The opposite happens at a positive angle, where the toe-in alignment of the wheels forms a Λ, projecting the wheel angle inward.
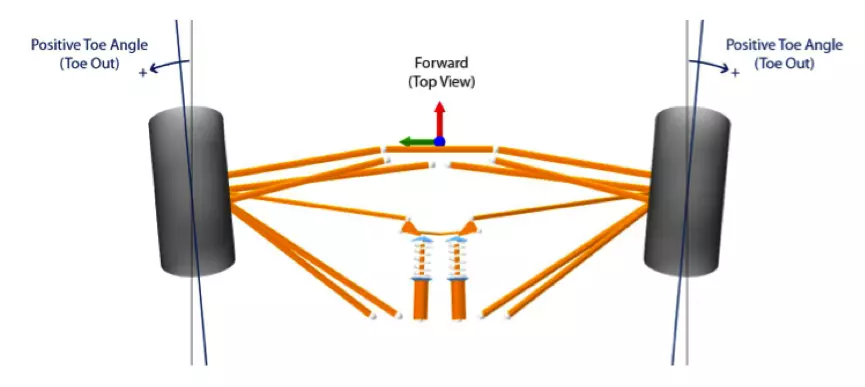
How does the ZF AKC system manage to vary the toe-in angle on the rear axle wheels?
Like systems of the past, all use hydraulic or electro-hydraulic actuators. ZF's is electrohydraulic and has two distinct forms: or as central or double actuator . In the case of high-performance vehicles, electro-hydraulic actuators placed on the suspension of each wheel are used.
In fact, when vehicles are equipped with dual actuators, they replace the upper suspension arm, where another crosslink arm joins the upper arms. The operation of the actuators responds directly to inputs from the ECS control module which, in real time, varies the angle of convergence of the rear axle wheels.

How does the ZF AKC system work?
As already mentioned, the input we give to the steering wheel, front wheel turn angle and speed, allows the ECS control module to determine the variation of the active steering system. In practice, at low speed or in parking maneuvers, the active steering system varies the angle of the rear wheels in the opposite direction to the front, reducing the turning angle and favoring parallel parking.
When driving at higher speeds (from 60 km/h) the feats of the active steering system ensure more stability in corners. At this stage the rear wheels turn in the same direction as the front wheels.
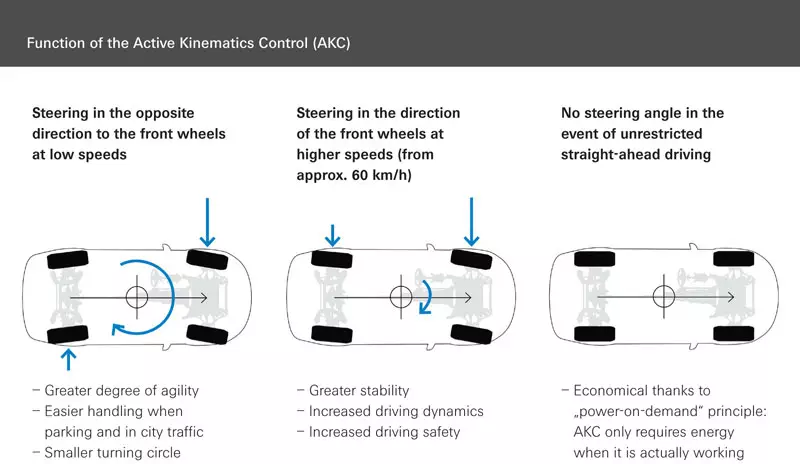
When the vehicle is driven without any steering wheel movement, the control module automatically assumes that it is not in use, thus saving energy consumption. In fact, ZF's active steering system is a “Steering on Demand” system, but also a “Power on Demand” system.
ZF took years to democratize this active steering system and Porsche was one of the first manufacturers to assemble this new generation of active steering as a series in 2014. In 2015, after a year of maturing the system, Ferrari followed the same path. In the future it could be almost all sports models given the compatibility of the technical solution that ZF has developed.
