Dear readers, today we bring you another study, published by Transport&Environment, which reveals surprising facts regarding particulate emissions from cars with direct gasoline injection.
It is estimated that in Europe alone, air pollution is responsible for 406,000 deaths annually, behind this we have 100,000 working days lost to sick leave and a cost to the economy of around 330 to 940 million per year.
Small particles present in the atmosphere are of great risk to public health as they penetrate deeper into the lungs, being absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a variety of diseases and even death. The O.M.S has recently confirmed that air pollution is one of the causes of the appearance of cancer cases. More than 90% of the EU population is exposed to levels of particulate pollution, which pose a real health risk, and around 1/3 of all EU citizens are exposed to particulate pollution far above allowable levels. by Community directives.
As is well known, particles are also a direct cause of global warming, through black carbon residues released into the atmosphere. In the U.E about 1/5 of all fine particles are mainly emitted by diesel vehicles. But the tests carried out by the TUV and the tests by the NDEC system (New European Drive Cycle), show that after all direct injection gasoline engines are even more polluting than modern diesel vehicles.
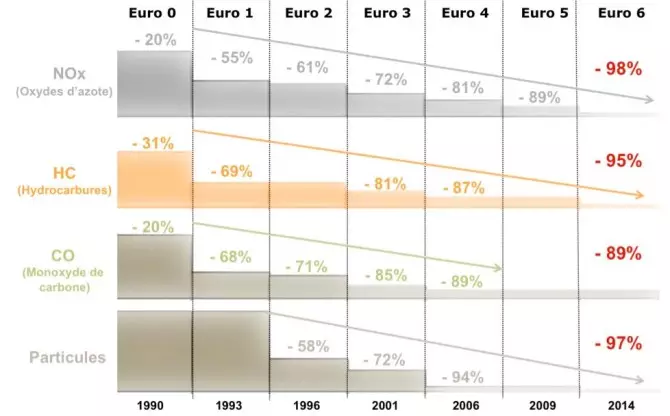
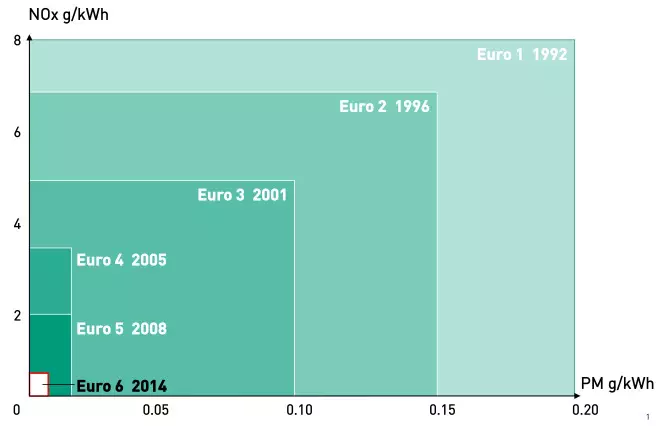
One of the questions that arises in this situation is whether the GDI (Gasoline Direct Injection) engines will be able to meet the strictest environmental standards in the future. The limits and environmental standards in force in Europe have been reduced and another standard will soon be introduced, EURO6. However, all new vehicles that are sold on the European market must prove that they are properly regulated and that they comply with the regulations in force. But in fact, despite all this tight legislative scrutiny, part of this alleged hoax is in the way manufacturers pass emissions approvals for their vehicles. In practice, for example, Diesel vehicles emit more NOx (nitrogen oxide) on the road than in tests in a controlled environment. Until recently, gasoline cars were considered to be of low impact as far as particle emission was concerned, but with the introduction of new technologies, such as direct gasoline injection, this allowed them to become even more efficient and lower. the resulting CO2 emissions.

GDI engines are expected to gradually start replacing all MPI engines by 2020 and to reverse the diesel market trend. Another estimate tells us that around 2030, the particles emitted by GDI engines will be greater than those emitted by Diesel engines. GDI engines, on average, emit 10 to 40 times more particulates per kg than MPI engines and 1000 times more particulates.
T&E commissioned the study, as we have already mentioned, to TUV, an independent auditor, with 3 different cars. The tests were carried out with a particulate filter installed and without a particulate filter.
The models in the test were the Ford Focus 1.0 ecoboost, the Hyundai i40 1.6GDI and the Renault Megane 1.2TCe Energy 115, all from 2013 and with mileages between 10,600 and 15,000km.

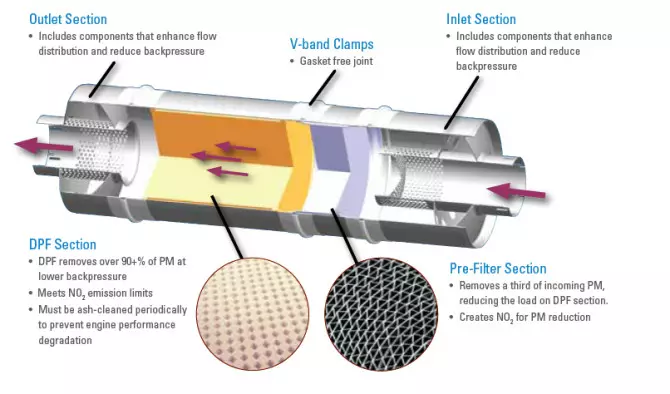
The final conclusions of this study showed that without the use of particulate filters, GDI engines clearly emit more emissions than more modern diesel engines. On the road, GDI engines can and do have the potential to surpass EURO 6 standards. The cost for manufacturers of equipping their GDI engines with a particulate filter is around €50, without any damage to consumption. Despite this obvious conclusion, most manufacturers continue to deny the introduction of particulate filters in their GDI engines, a situation that T&E warned about. T&E considers that manufacturers should not rely on the electronic management of their GDI engines as the only means of trying to control pollutant emissions, having been proven in road tests that, in fact, GDIs without filters emit much more particles to the atmosphere.

We know that there are a number of factors that actually have direct implications for the results that the study presents, and while we are also aware of the reluctance that still exists to provide GDI engines with particle filters, even in the case of cheap technology, on the other hand, it should be noted that part of the problem may be greater than what was thought.
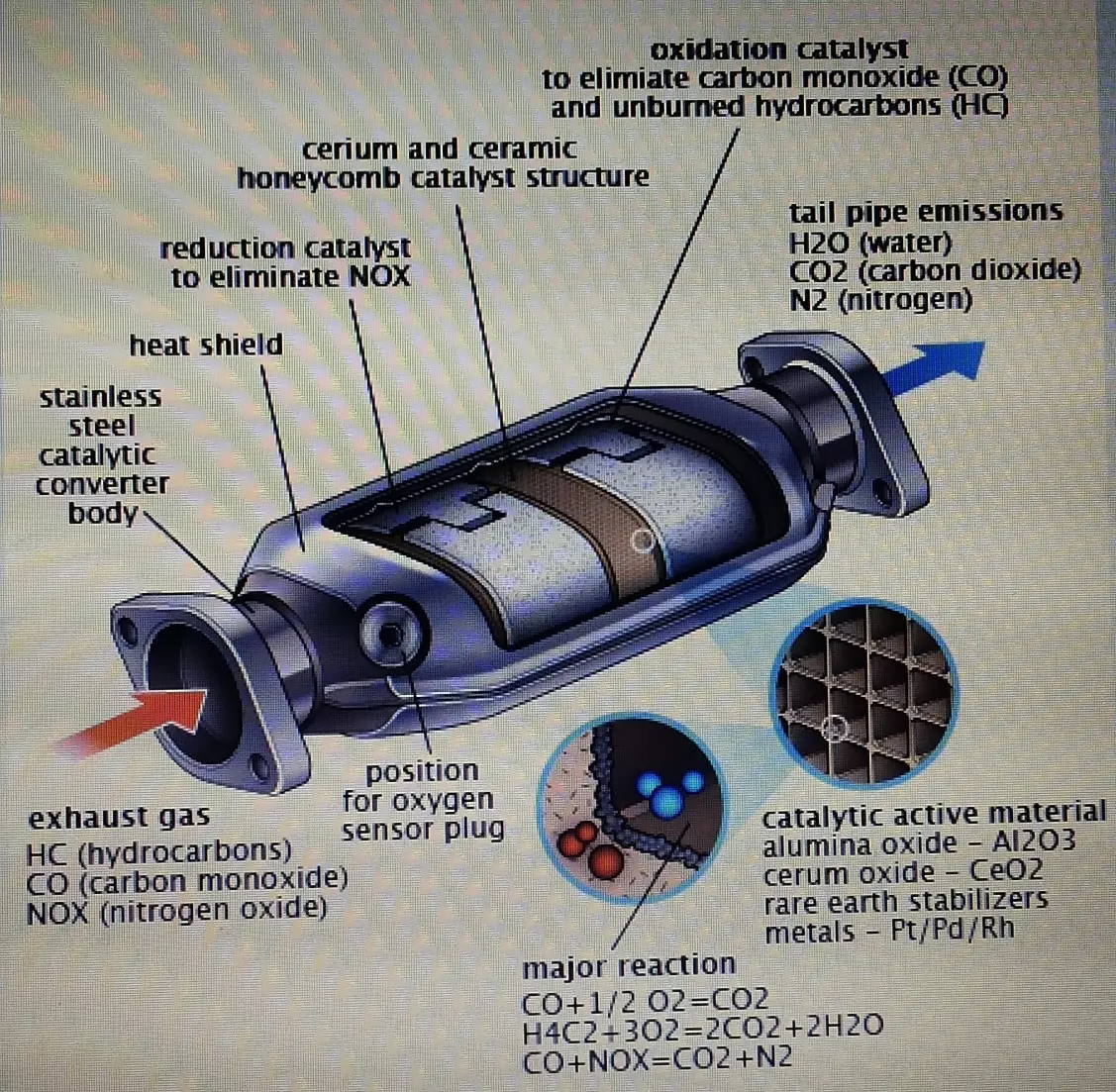
We may be facing a hoax when it comes to injection pressures, as the announced values of 2000bar upwards may not even be verified in reality – this is where a large part of the HC (Hydrocarbons) is reduced. Another detail has to do with the EGR valves, which are preponderant in the reduction of NOx (nitrogen oxide), but as a result of the performance that manufacturers want to give to the GDI blocks, they can have them with less restrictive electronic calibration. Finally, the other obstacle in this issue has to do with the catalytic converter, which is great for MPI blocks, being the main responsible for the decomposition of CO (carbon monoxide), but which does not result in GDI, since the ceramic mesh it is less dense than the filter element in particulate filters.
Here's the link to the TUV report and the T&E briefing so you can see the test in more detail.
Clearly something is not right and if Diesels no longer live without particulate filters, this step will also have to be taken in GDI's. Builders need to cling more to what is already proven, rather than go through trial and error in search of the ideal solution.