The Start/Stop system as we know it came much earlier than you think. The first emerged in the 70s, at the hands of Toyota, during a period when oil prices were increasing significantly.
Because most automobiles at that time used carburetors, the system was not successful. The time the engines took to start and the operating problems they presented, so dictated.
Volkswagen was the first to introduce the system en masse in several models such as the Polo and Passat, in versions called Formel E, in the 80s. After that, apparently only in 2004 did an implementation of the system appear, manufactured by Valeo and applied to the Citroën C3.
Certain is that currently the Start/Stop is transversal to all segments, and you can find it in townspeople, family, sports, and anything else you can imagine.

Bearing in mind that for a modern gasoline engine, the fuel consumed for the hot start is the same as that needed for 0.7 seconds at idle , we easily realized the usefulness of the system.
In practice it makes sense, and it is considered one of the best systems to save fuel , but the question arises frequently. Will a system be beneficial in the long term for the engine's life? It's worth a few more lines for you to understand.
How it works
The system was designed to end situations in which the vehicle is immobilized, but with the engine running, using fuel and emitting polluting gases. According to several studies, these situations represent 30% of the usual routes in the city.
Thus, whenever immobilized, the system turns off the engine, but the car keeps almost all other functions active. Like? There we go…
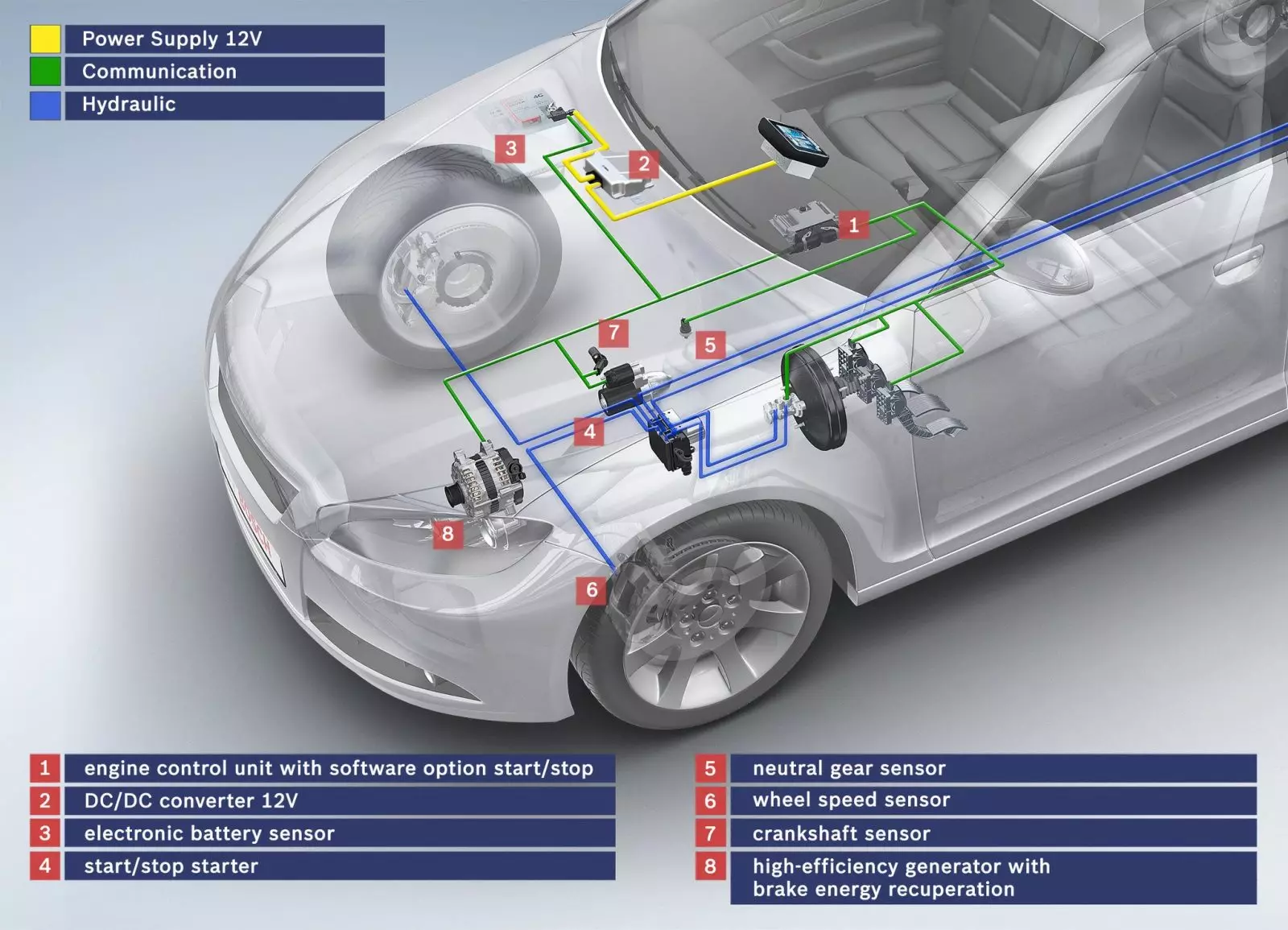
Entering Start/Stop is not just an option that allows you to turn off the engine. To be able to rely on this system, other components are needed, which not only allow it to function but also ensure that it does not generate any problems.
Thus, in most cars with Start/Stop system we have the following additional items:
Engine start and stop cycles
A car without Start/Stop goes, on average, through 50 thousand stop and start cycles of the engine during its life. In a car with the Start/Stop system, the value rises to 500,000 cycles.
- Reinforced starter motor
- Larger capacity battery
- Optimized internal combustion engine
- Optimized electrical system
- More efficient alternator
- Control units with additional interfaces
- Additional sensors
The Start/Stop system does not switch off the car (ignition), it only switches off the engine. This is why all the other functions of the car remain in operation. For this to be possible, an optimized electrical system and a larger battery capacity are needed, so that they can withstand the operation of the car's electrical systems with the engine off.

Thus, we can consider that the "greater wear of components" due to the Start/Stop system it's just a myth.
Benefits
As advantages we can highlight the main purpose for which it was created. Saving Fuel.In addition to this, the inevitable reduction of polluting emissions when the car is immobilized, it's another advantage, because there can also be a reduction in road tax (IUC).
THE silence and tranquility that the system allows the engine to be turned off in traffic whenever it is stopped, but apparently not, is also significant, since we no longer have any type of vibrations and noise caused by the engine during the time we remain immobilized.
Disadvantages
It is possible to consider that there are no disadvantages in using the system, since it is always possible to turn it off. However, when this is not done, we can have some hesitation in starting, although the systems are more and more evolved and allow increasingly smoother and more immediate engine starts.
In the useful life of a car, the battery price , which as mentioned are bigger and with a superior capacity to support the system, being also considerably more expensive.
There are exceptions
The introduction of the Start/Stop system has forced manufacturers to ensure that the engine is capable of withstanding several successive stops when the system starts up. For this, the system works with several conditions that, if not verified, inhibit the system, or suspend it, namely:- engine temperature
- Use of air conditioning
- outdoor temperature
- Steering assistance, brakes, etc.
- battery voltage
- steep slopes
To switch off? Why?
If it is true that for the system to be activated it is necessary to fulfill a series of requirements such as having the seat belt fastened, and having the engine at an ideal temperature, among others, it is also true that sometimes the system is activated without some of the requirements fulfilled.
One of the requirements for the system not to go into operation has to do with the fact that ensure lubrication, cooling and cooling . That is, after a long journey, or a few kilometers at a higher speed, it is not at all convenient for the engine to be switched off abruptly.
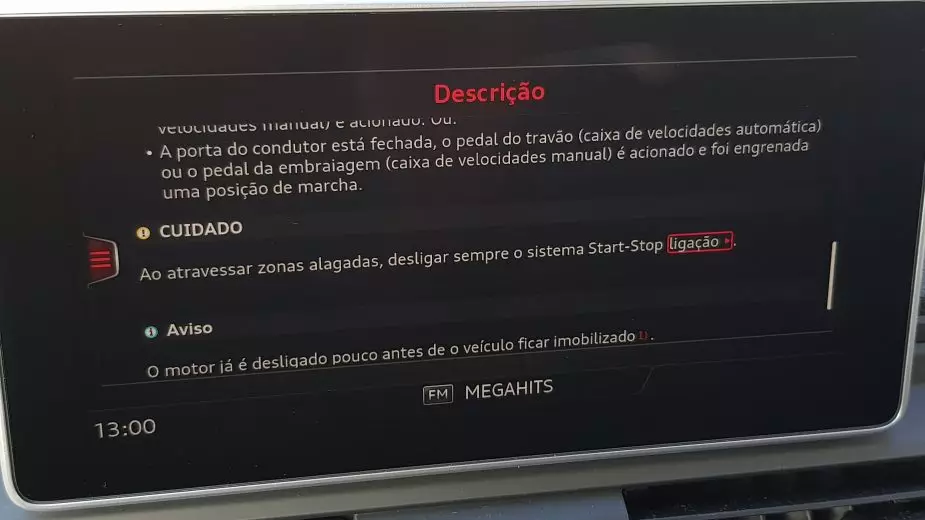
This is one of the situations where you must shut down the system , so that the engine is not switched off immediately at stops following a long or “hurried” journey. It also applies to any stressful situation, sporty driving or on a circuit. Yes, on those track-days I strongly advise you to ensure that the system is turned off.
Another situation is when driving off-road, or for example in a flooded area at the time of heavy rain. Once again it's obvious. The first is because the crossing of obstacles is sometimes done at such a low speed that the system will turn off the engine, when in fact we want to advance. The second is that, in the event that the exhaust pipe is under water, when the engine starts, the water is sucked through the exhaust pipe, causing damage to the engine that may prove irreparable.
Consequences?
These situations, which we have just mentioned, can cause some possible problems, especially in supercharged (with turbo) and high power engines — Turbos not only achieve rotation speeds above 100,000 rpm , how can they reach temperatures of large hundreds of degrees centigrade (600 °C – 750 °C) — Thus, it is easy to understand what happens when the engine stops abruptly. Lubrication is suddenly stopped, and the thermal shock is greater.
However, and in most cases particularly in day-to-day and when driving in cities, the Start/Stop systems are designed to support the entire life of the car, and for that all components that may suffer a greater wear with this system are reinforced.
