The car's alternator is one of the most important components of combustion-engine cars—although electric cars also have a component for the same purpose.
That said, the engine alternator is a component that transforms kinetic energy — produced by engine motion — into electrical energy. Electricity that is used to power the car's electrical system and all associated systems. Some of this electrical energy is used to charge or maintain a battery charge.
With the electronic complexity of modern automobiles, the alternator has become a fundamental component for the functioning of automobiles. Without him, you're not going anywhere. You'll understand why.
How does the alternator work?
As mentioned, the alternator is an electrical machine that transforms kinetic energy into electrical energy.
The engine alternator consists of a rotor with permanent magnets (see image), connected to the engine crankshaft through a belt.
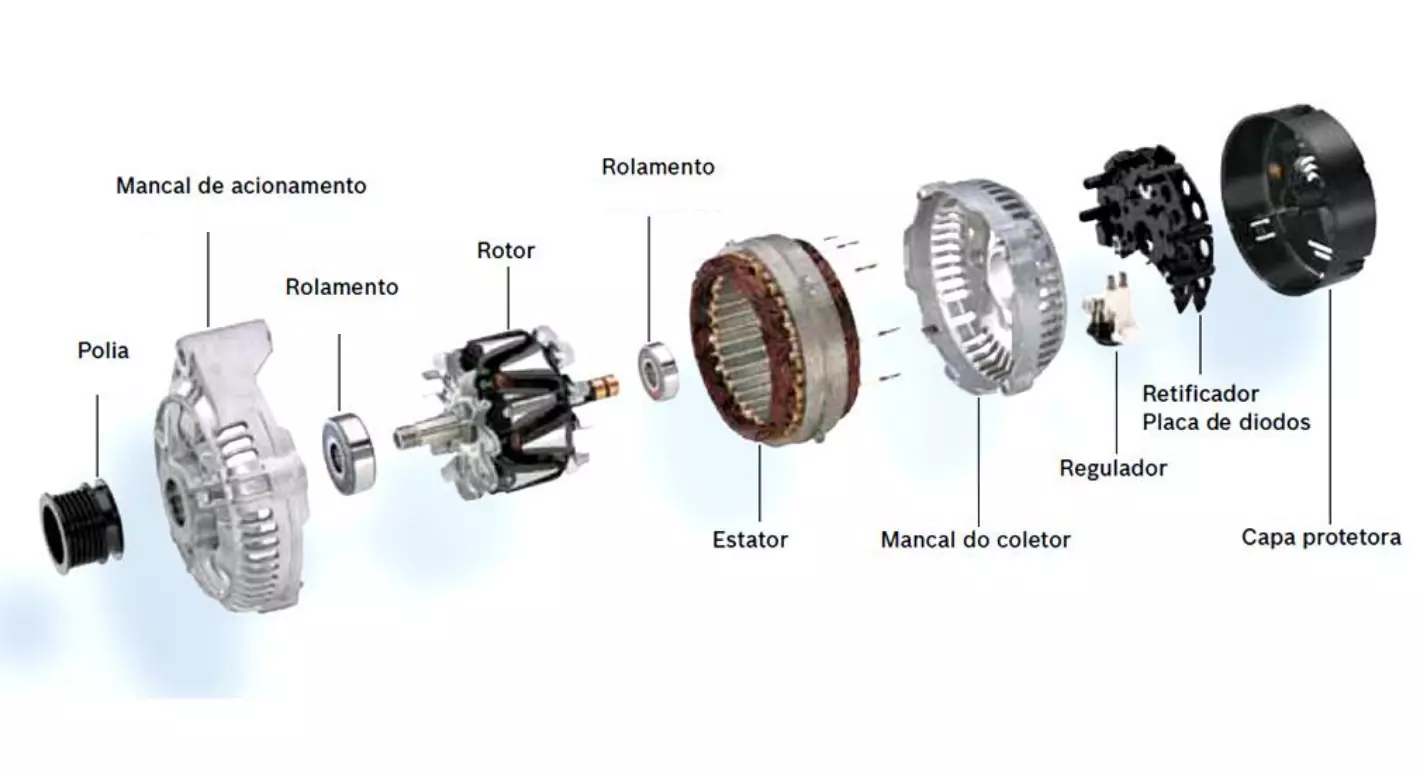
This rotor is surrounded by a stator, whose magnetic field reacts to the rotating movement of the rotor induced by the crankshaft, generating electrical current in this process. As it depends on the crankshaft rotation, the alternator only generates electricity when the engine is running.
On the rotor shaft there are brushes that send the generated electricity to the rectifier and voltage regulator. The rectifier is the component that transforms alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) — the current that is compatible with a car's electrical systems. The voltage regulator adjusts the output voltage and current, making sure there are no spikes.
What is the alternator's function?
Most modern automobiles run on a voltage of 12 V (Volts). Lights, radio, ventilation system, brushes, etc.
When the car is off, it is the battery that powers all these components. When we start the engine, it is the alternator that starts performing this function and replenishing the charge in the battery.
Cars with 48 V system
The most modern cars — nicknamed mild-hybrid, or if you prefer, semi-hybrid — use parallel 48 V electrical systems. They are not equipped with a conventional alternator.
In these cars, the alternator gives way to an electric machine, whose operating principle is similar, but takes on other functions:
- Generating charge for a high-voltage battery — the energy consumption of modern cars is higher due to their electronics;
- Assist the combustion engine in acceleration and recovery — the energy stored in the high voltage battery is used to boost power;
- It serves as a starter motor — since it has a dual engine/generator function, it replaces the starter motor;
- Frees the combustion engine — in cars with a 48 V system, components such as power steering, air conditioning, or driving support systems are directly dependent on this system to free the engine for its main function: moving the car.
In electric cars, the conventional alternator doesn't make sense because we have the batteries — so there's no need to generate electrical current to power the car's systems. However, braking and decelerating electric car engines also operate on the same principle as alternators: they transform kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Do you want to see more articles on automotive technology and components? Click here.
- After all, are three-cylinder engines good or not? Problems and advantages
- 5 Reasons Diesels Make More Torque Than Gas Engines
- Everything you need to know about the clutch
- Volumetric compressor. How it works?
- What are CV joints?
